USA Emerged : A number of important historical events led to the formation of the United States of America. Let’s examine its voyage:
Native Americans and Colonization:
- About 15,000 BC, the first humans arrived in the Americas, marking the beginning of the history of the regions that would eventually become the United States. These native people most likely crossed the Bering Strait to move from Asia to North America.
Arrival and Independence of Europe:
- In 1776, the colonies proclaimed themselves independent and established the “United States of America” during the Second Continental Congress in Philadelphia.
- This historic occasion heralded the creation of a new nation that would later be molded by the American Revolution, the Constitution’s drafting, and the installation of a federal government.
Economic Power and the Industrial Revolution:
- The Industrial Revolution, which took place between the late 18th and early 19th centuries, led to the United States becoming a global economic force.
- The nation’s economy grew quickly due to technological, manufacturing, and transportation innovations, which made it a major player on the world stage.
Wars, Expansion, and Modern America
- Territorial expansion, the American Civil War, two World Wars, and profound social and cultural shifts were all experiences in the 19th and 20th centuries.
- The United States changed into a diversified and powerful country from the Louisiana Purchase to the Cold War era, influencing the path of world history.
The development of the United States of America is a complex tale of resiliency, invention, and advancement.

Journey to becoming a superpower.
The US started a spectacular path to becoming the world’s most powerful nation. Let’s examine the crucial periods that influenced its rise:
Origins of Colonialism and Expansion:
- The US was once isolated when it was founded as a colony. But its whole nature was expansionism, propelled by land acquisition and westward territorial extension.
- The abolition of the slavery debate during the Civil War cleared the path for additional immigration outside of North America.
Centralization and the Industrial Revolution:
- The Industrial Revolution accelerated economic expansion, making a more centralized government necessary to oversee it.
- The US was able to gain territory abroad through concentrated power in the executive branch, which resulted in the Spanish-American War of 1898.

After-World War II Impact:
- The United States emerged as the only major power with both economic and military might following World War II.
- Through organizations like the United Nations (maintaining peace) and the Bretton Woods system (coordinating the world economy), it built the postwar order.
- The US created NATO, increased its worldwide footprint, and became involved in conflicts all over the world to confront the Soviet threat.
Lasting Promises:
- Realizing their importance in sustaining peace and prosperity, the US upheld its foreign obligations and alliances even after the demise of the Soviet Union.
The United States’ transformation from colony to superpower is evidenced by its current status as the most interconnected and significant power in the world.
USA Emerged as military superpower.
On the international scene, the United States of America (USA) is a powerful military superpower. Let’s examine the causes of its unmatched military might:
World Firepower Ranking:
- The United States of America is always ranked first on the Global Firepower (GFP) index. Among the 145 countries evaluated for the 2024 GFP review, the United States is ranked first.
- Its commanding values across the main material, financial, and resource categories are reflected in its PwrIndx score of 0.0699.
Important Elements Affecting US Military Dominance:
- Financial Resources: Defense is given a large amount of funding by the United States. It spent an astounding $778 billion in 2020, which accounted for more than one-third (39%) of all defense spending worldwide.
- Technological Edge: The USA is a leader in the development of cutting-edge military technologies, such as cyber capabilities, space-based systems, and sophisticated weaponry.
- Global Reach: What distinguishes it from other countries is its capacity to organize, launch, maintain, and engage in combat over land, sea, air, and space.
- Nuclear Arsenal: The 1968 Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) does not absolve the United States of its status as a major nuclear power.

Continuity in History:
- The USA has consistently shown its military might by holding the top spot in the GFP for 18 years running.
- As one of NATO’s founding members, it actively promotes international security.
Strategic investments, technological advancement, and an unrelenting dedication to defending its interests and international stability have contributed to the United States’ military superiority.
The following are the top military powers in the world as of 2024, according to the Global Firepower (GFP) rating, which takes into account over 60 parameters, including military units, financial position, logistical capabilities, and geography:
- United States (USA): With a PowerIndex (PwrIndx) score of 0.0699, it was ranked first.
- Russia: With a PwrIndx score of 0.0702, it was ranked second.
- China: With a PwrIndx score of 0.0706, it was ranked third.
- India: With a PwrIndx score of 0.1023, it came in fourth place.
- South Korea: With a PwrIndx score of 0.1416, it came in fifth place.
Although the USA is unmatched in its military might, other countries like China, India, and Russia are also very powerful. Remember that each country’s particular circumstances influence its military might and that this rating takes conventional fighting capabilities into account.
What are the military weapons and technology of the USA?
To maintain its status as a world powerhouse, the United States of America (USA) has continuously pushed the frontiers of military technology. Let’s examine some of the state-of-the-art tools and equipment that the US military uses.
AI-powered autonomous drones:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) has been integrated into next-generation drones, enabling them to track enemy activity and fly on their own.
- These drones function in any condition and give operators access to real-time video feeds and intelligence.
3. Facial recognition technology improves precision targeting and reduces collateral damage by assisting in the identification of friendly or hostile persons.
Drones powered by lasers:
- Drone capabilities are made more sophisticated by laser technology. Like hellfire missiles, lasers are deadly fast and provide accurate engagement.
- These lasers effectively neutralize vehicles, planes, and weapon systems by penetrating targets with extreme heat.
Platforms for Next-Generation Weapons (2023):
1. Optionally Manned Fighting Vehicles: Combining human and autonomous capabilities for increased combat effectiveness. The US Army plans to introduce 24 signature systems by 2023.
- Long-range hypersonic weapons: These weapons can hit with extreme precision and speed.
Space Dominance and Cyberwarfare:
- To maintain its dominance in the digital sphere, the USA makes significant investments in cyber capabilities.
- Space-based systems are essential for navigation, communication, and surveillance.
Advanced Personal Equipment and Armor:
- The US military uses cutting-edge helmets, body armor, and protective gear.
- Survivability, communication, and situational awareness are improved by soldier-worn devices.
DEWs, or directed energy weapons:
DEWs, such as microwave systems and high-energy lasers, provide scalable and accurate firepower.
- Without utilizing conventional ammo, they are able to neutralize drones, missiles, and other threats.
The United States of America allocates funds towards medical research, sophisticated prostheses, and trauma care.
- Advances in biomedicine enhance the health and resiliency of soldiers in combat.
The USA’s military arsenal comprises state-of-the-art equipment, a clear strategic direction, and an unflinching dedication to upholding its status as a military superpower.
USA Emerged defence system.
Different elements of the American defense force:
Combat Aircrafts:
A formidable fleet of fighter jets is operated by the United States Air Force (USAF). Some of the main fighter aircraft in service as of 2023 are as follows:
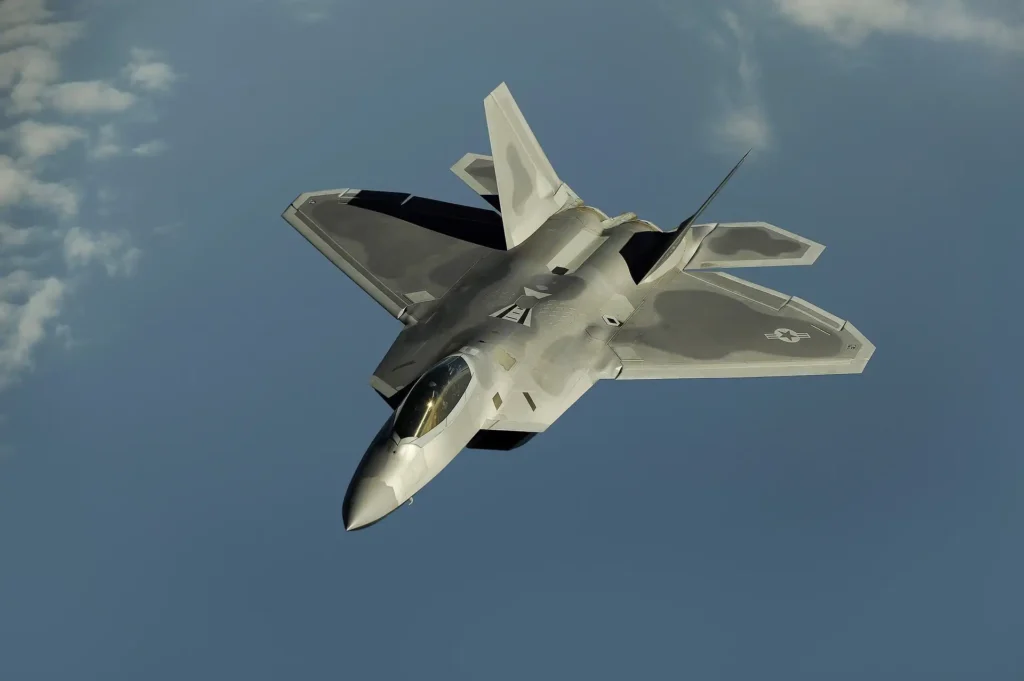

F-22 Raptor:
An American single-seat, twin-engine, stealthy, multirole combat aircraft that can fly in all weather conditions is the Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor. The following are some important details:
Function: The F-22 Raptor is engineered to perform strike missions in addition to air superiority. It combines exceptional situational awareness, sensor fusion, and stealth.
Manufacturer: Northrop Grumman and BAE Systems are the main partners of Lockheed Martin, which is the prime contractor.
Alternatives:
F-22A: The version for conventional takeoff and landing (CTOL).
F-22B: A version that uses short takeoff and vertical landing (STOVL).
F-22C: Version based on carriers (CV/CATOBAR).
Technical details (F-22A):
Thrust: each engine is 35,000 pounds.
Wingspan: 13.6 meters, or 44 feet, 6 inches.
Length: 18.9 meters, or 62 feet, 1 inch.
Height: 5.1 meters, or 16 feet, 8 inches.
Weight: 19,700 kilos (43,340 pounds). Maximum takeoff weight: thirty-eight thousand pounds (83,500 kg).
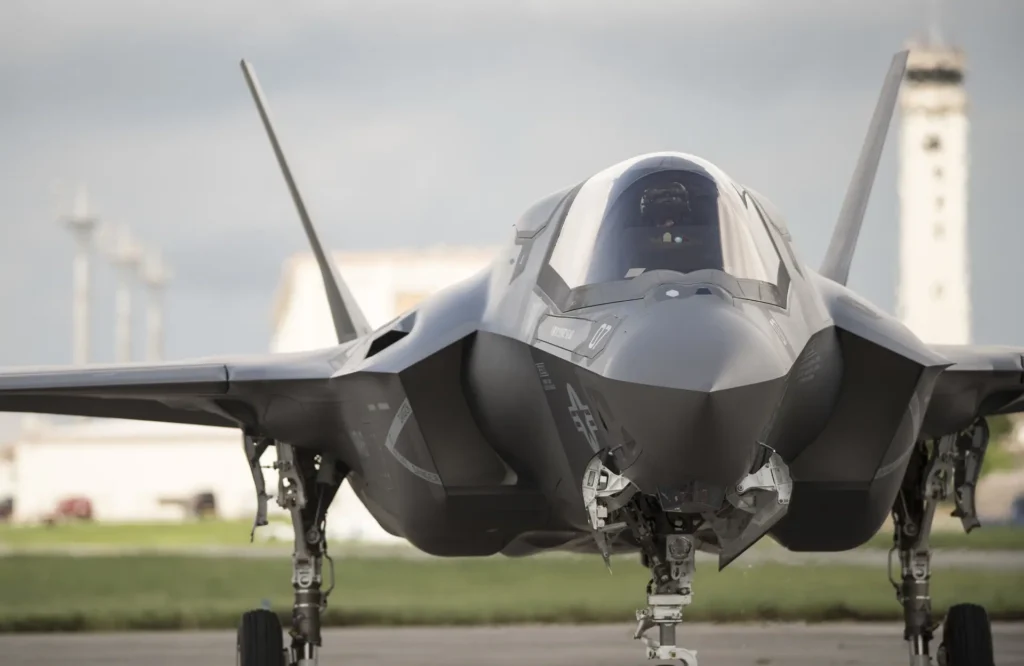

F-35 Lightning II:
A family of fifth-generation, single-seat, multirole combat aircraft manufactured by Lockheed Martin. The highlights are as follows:
Role: The F-35 Lightning II is used for information, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR), air superiority, strikes, and electronic warfare operations.
The F-35A is a derivative that uses conventional takeoff and landing (CTOL) technology.
F-35B: Vertical landing and short takeoff (STOVL) variant.
F-35C: Model based on carriers (CV/CATOBAR).
Origin: Based on the Lockheed Martin X-35 development.
made its first flight in 2006.
commenced duty in July 2015 with the U.S. Marine Corps (F-35B), then in August 2016 with the U.S. Air Force (F-35A), and in February 2019 with the U.S. Navy (F-35C).
Planned Usage: Through 2044, the United States intends to purchase 2,456 F-35s, making them a vital component of NATO and American-allied air power.
anticipated to run until 2070.
The A-10 Thunderbolt II (Warthog) of the Fairchild Republic:
- A ground attack plane intended for close-quarters combat.
- It is well-known for its dependability and capacity to function in low-altitude conditions.
- There are about 5,000 operational A-10s and more units that are stored.
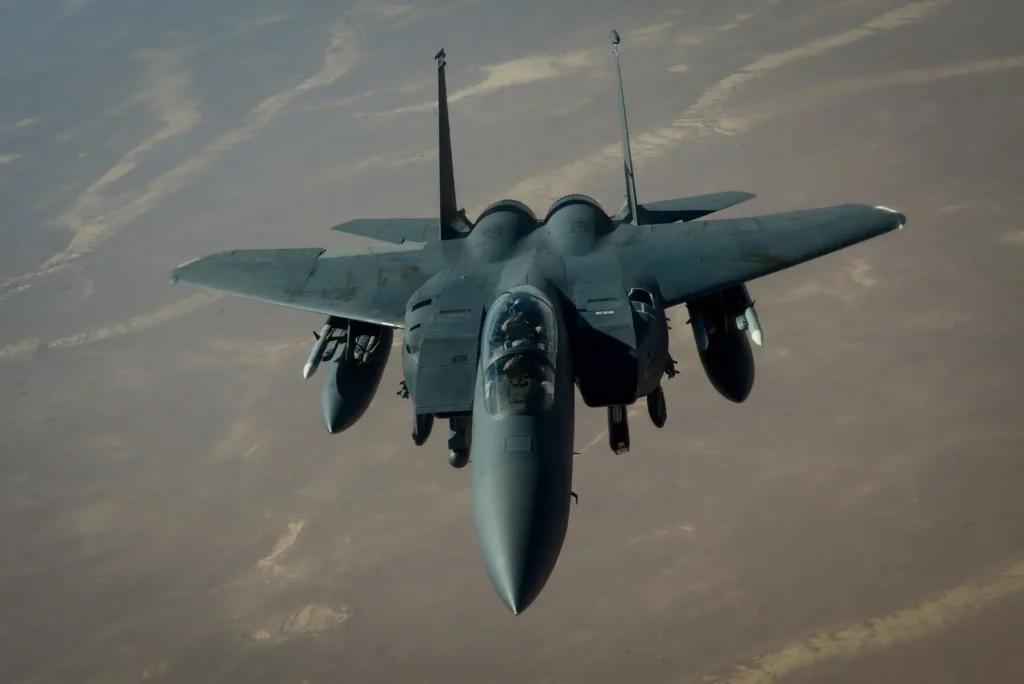

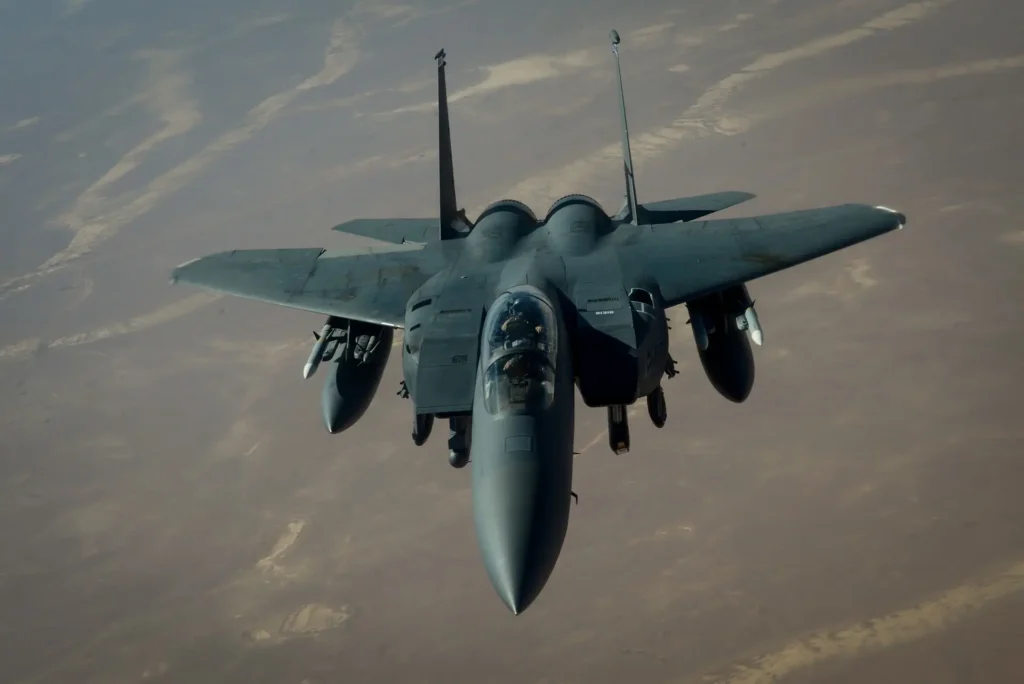
F-15 Eagle McDonnell Douglas:
- A fighter with diverse air superiority.
There are 2.266 F-15 Eagles in use.
3.218 F-15E Strike Eagles are in service, and another 104 are on order.
4.2 F-15EX Eagle II Boeings.
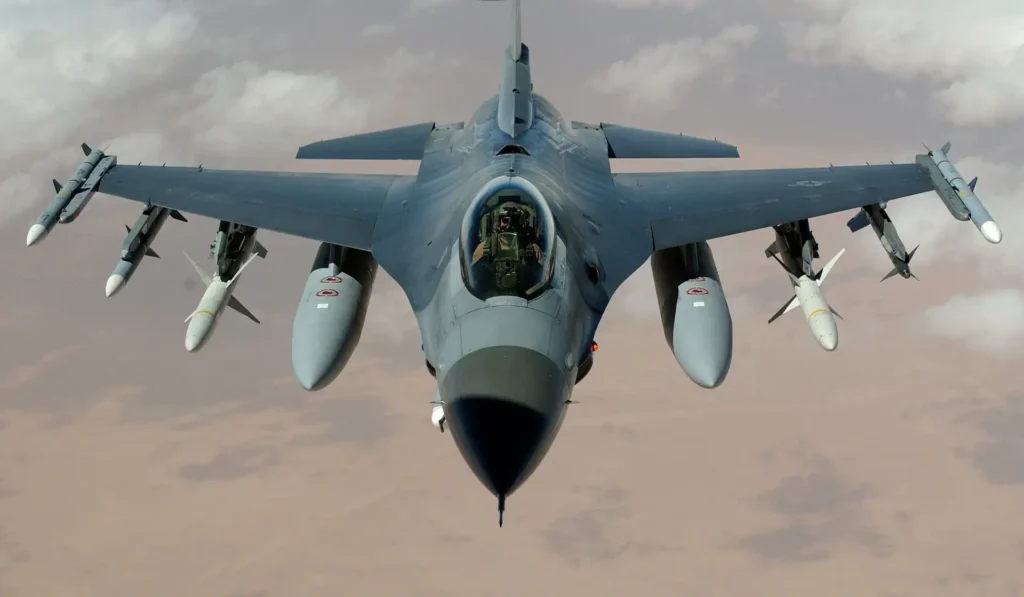

the F-16 Fighting Falcon from Lockheed Martin:
A multipurpose fighter utilized by the United States Air Force and its allies.
F-16 Fighting Falcons with 2.922 active.
Artillery: For both combat and support, the U.S. Army uses a variety of artillery systems.
The M270 MLRS, or Multiple Launch Rocket System:
- An extremely mobile system for rocket artillery.
- Able to fire several rockets with precise guidance.
- Offers efficient firepower and quick reaction times.
M1 Breacher Vehicle for Assault:
- Used to get around barriers and minefields.
- Outfitted with a charge system for mine-clearing lines.
M1097A2 Unarmored Carrier for Air Defense, Troops, and Goods:
- A multipurpose vehicle for moving freight and troops.
Tanks: The U.S. Army possesses the following tanks:
Main Battle Tank, M1 Abrams:
- There are about 5,000 M1 Abrams tanks in service.
- A recognizable tank renowned for its protection and firepower.
M1A2B/C SEP v3 and M1A1 AIM.V2/SA:
- M1 Abrams upgraded versions.
Lightweight Storage Tanks:
- M10 Booker and its modifications.
Nuclear Weapons: To preserve deterrence, the United States keeps a strong nuclear triad:

Land-Based ICBMs:
Over 10,000 employees oversee up to 400 LGM-30G Minuteman III ICBMs in five states’ worth of hardened silos.
Ballistic missiles launched from submarines (SLBMs):
Installed on submarines of the Ohio class.
Bombers with a strategic aim:
- Bombers B-2 Spirit and B-52 Stratofortress.
The M142 HIMARS system is one of the rocket launchers used by the U.S. Army, which also uses other launchers for rockets that are precisely guided.
Keep in mind that this is only a high-level summary and that American defense capabilities are vast and ever-changing.
Sixth-generation fighter aircraft development is a current endeavor of the United States. The salient features are as follows:
NGAD, or Next Generation Air Dominance:
- The endeavor is being spearheaded by the U.S. Air Force through its Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) program.
- The goal of NGAD is to deploy a “family of systems” as the next-generation air superiority platform, replacing the Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor.
- Because the program is top secret, very little information is provided to the general public.
Development, Manufacturing, and Engineering (EMD):
- The sixth-generation fighter’s EMD program has been formally launched by the Air Force.
- Eventually, the development aircraft will be produced.
- By the end of the decade, the Air Force expects to have the capacity.
Prototype and Mitigation of Risk:
- The Air Force conducted NGAD fighter experimental prototype flight testing in 2020.
- The goal of this prototype was to lower the risks related to important technologies required for a manufacturing program.
Principal Contractor:
- The identity of the prime contractor in charge of creating the sixth-generation fighter is still unknown.
- Lockheed Martin, Boeing, and Northrop Grumman are likely contenders.
- Lockheed Martin is a formidable competitor given its background in creating the fifth-generation F-22 and F-35 stealth fighters.
- Boeing could possibly be involved; however, it’s still unclear if they’ll be able to design a completely new combat aircraft.
Modern technology is embodied in the USA’s sixth-generation fighter program, which will be essential to their future air superiority.
USA Emerged Necluer Weapons Program.

The development and use of nuclear weapons have a lengthy and noteworthy history in the United States. Let’s examine some important facets of the US nuclear program:
- Development and Testing: The United States of America was the pioneer nation to produce nuclear weapons.
Between 1945 and 1992, 1,054 nuclear tests were carried out by it.
During World War II, the first atomic weapons were successfully developed, thanks to the Manhattan Project.
The Cold War escalated the nuclear arms race between the US and the USSR as they fought for dominance.

2. Stockpile and Arsenal: Since 1945, the United States of America has manufactured more nuclear warheads—more than all other nuclear weapon states combined—than any other country.
By 2023, the United States of America would have had about 3,708 warheads in its arsenal.
A strong and varied capacity is guaranteed by the nuclear triad, which consists of strategic bombers, land-based missiles, and missiles launched from submarines.
- Testing and Fallout: Following the passage of the Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, the majority of early American nuclear tests were carried out underground.
Affected groups have received compensation, including Marshall Islanders and US individuals who were exposed to radioactive risks.
- Strategic Importance: The United States and Russia jointly own more than 90% of the world’s nuclear weapons arsenal. The U.S. nuclear arsenal guarantees national security and acts as a deterrent against adversaries.
In conclusion, the United States’ nuclear program has influenced world geopolitics and continues to be a vital part of its security plan.
USA GDP in the past 5 years.

The United States saw strong economic growth in 2023. The following are salient features of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the United States:
Real GDP Growth: The Bureau of Economic Analysis’s “advance” estimate for the fourth quarter of 2023 states that the US economy grew at an annual pace of 3.3%. This expansion came after the real GDP grew by 4.9% in the third quarter.
Those who facilitate growth:
The expansion in the GDP was driven by increases in consumer spending, exports, state and local government expenditure, nonresidential fixed investment, federal government spending, private inventory investment, and residential fixed investment.
The GDP is calculated by deducting imports, which also grew.
GDP in Current Dollars: In 2023, the GDP in current dollars climbed by 6.3% to $27.36 trillion.
This growth is a reflection of all economic activity, including fluctuations in prices.
Second Estimate: On February 28, 2024, the “second” estimate for the fourth quarter—which is based on more comprehensive data—will be made public.
In general, the American economy showed resiliency and encouraging momentum in 2023.
The US GDP (gross domestic product) throughout the previous ten years:
1. 2022: The GDP of the United States was $25,462.70 billion, a 9.21% rise over 2021.
2. 2021: The GDP of the United States was $23,315.08 billion, up 10.71% from 2020.
3. 2020: The U.S. GDP decreased by 1.5% from 2019 to $21,060.47 billion.
4. 2019: The GDP of the United States was $21,380.98 billion, up 4.13% from the previous year.
Major political parties in the USA.
Although there are several political parties in the US, the Democratic Party and the Republican Party are the two largest ones. This is a synopsis of these significant parties:
Party of Democracy:

- American social liberalism is the ideology.
- Established in 1828.
- There will be roughly 47.2 million members by 2022.
- Joe Biden won the 2020 presidential election.
- Senators: 51 out of 100 in 2023.
- Representatives: 212 out of 435 in 2023.
Governors (2023): three of the six. - State Legislators: 3,271 of 7,383 in 2023.
In 2023, 19 out of 49 states were Trifectas.

The Republican Party
- American conservatism is the ideology.
- Established in 1854.
- The projected membership in 2022 is 35.7 million.
- Donald Trump won the 2020 presidential election.
- Out of 100 senators, 49 are in 2023.
- Representatives: 222 of 435 in the year 2023.
Governors (2023): three of the six. - State Legislators: 4,031 of 7,383 in 2023.
- Trifectas (2023): 28 states total, including 49.
The political landscape of the country is shaped by these two major parties, whose policies, candidates, and ideologies have a significant impact on important choices made at the federal and state levels.
USA dominance over other countries.

In the past, the US has dominated and had considerable influence on the international scene. Let’s examine a few facets of American dominance:
Military Domination:
- The United States has the strongest military in the world.
- It upholds an extensive global network of military installations.
- The United States military is present in almost 40% of the countries on Earth.
Power Economy:
With an economy that makes up almost 30% of global wealth, the United States has the greatest economy.
- It dominates the global banking system and maintains control over vital sea lanes.
Leadership in Technology:
- The American armed forces and those of other nations are significantly separated by U.S. weaponry technologies.
- The United States’ military dominance is bolstered by precision-guided missiles, supercarrier groups, sophisticated satellite systems, and military space dominance.
Cultural Impact:
- American music, fashion, technology, and film influence world culture.
- When it comes to worldwide communication, English continues to rule.
Mild Power:
- The United States upholds freedom of speech, human rights, and democratic principles.
- Students come to American institutions from all around the world.
But there are obstacles, such as emerging nations like China, shifting geopolitical landscapes, and shifting alliances. Future American dominance will hinge on its capacity for flexibility, diplomacy, and strategic vision.


